Introduction: Understanding the 2200 Ohm Resistor
In the intricate domain of electronics, resistors are fundamental components that play a crucial role in managing electrical current. A 2200 ohm resistor is a specific value commonly used in various applications, ranging from basic electronics to complex circuits. Resistors limit the flow of electricity within a circuit. They adjust voltage levels, ensuring components function as intended. Understanding the characteristics and applications of the 2200 ohm resistor is vital, especially for students, hobbyists, and professionals working with electronics.
Resistors come in various values, and the choice of value often impacts a circuit’s performance. The 2200 ohm resistor is particularly popular due to its versatility in different circuit designs. As this article discusses, it is crucial to recognize how resistors affect overall functionality. This information is essential whether you are a beginner learning about electronics or an engineer designing advanced systems.
Characteristics of a 2200 Ohm Resistor
To effectively use a 2200 ohm resistor, it is vital to understand its key characteristics. Each resistor has unique specifications that determine how it interacts within a circuit. Firstly, tolerance is a critical specification. Tolerance indicates how much the actual resistance can vary from the stated value. For instance, a 2200 ohm resistor with a 5% tolerance can vary between 2090 ohms and 2310 ohms. Knowing this range is essential for applications that require precise resistance values.
Another significant characteristic is the power rating. This is measured in watts and indicates how much power the resistor can dissipate without overheating. Common power ratings for resistors include 1/8 watt, 1/4 watt, and 1 watt. For a 2200 ohm resistor, a power rating of 1/4 watt is common, making it suitable for most typical applications. However, exceeding the power rating can lead to failure or even damage to other components in the circuit.
The temperature coefficient is also important when choosing resistors. This specification indicates how the resistance changes with temperature variations. A resistor with a temperature coefficient of ±100 ppm/°C will change its resistance by 0.01% for every degree Celsius variation. This detail is particularly important in sensitive electronic applications where temperature stability is critical.
Different types of resistors are available, including carbon film, metal film, and wire-wound resistors. Each type has distinct advantages and disadvantages. For example, carbon film resistors are often more affordable and suitable for general use, but they may not offer the same level of precision as metal film resistors. Metal film resistors, on the other hand, offer better accuracy and stability but tend to be pricier. Finally, wire-wound resistors provide high power ratings but can be bulkier than other types.
Resistor Color Codes Explained
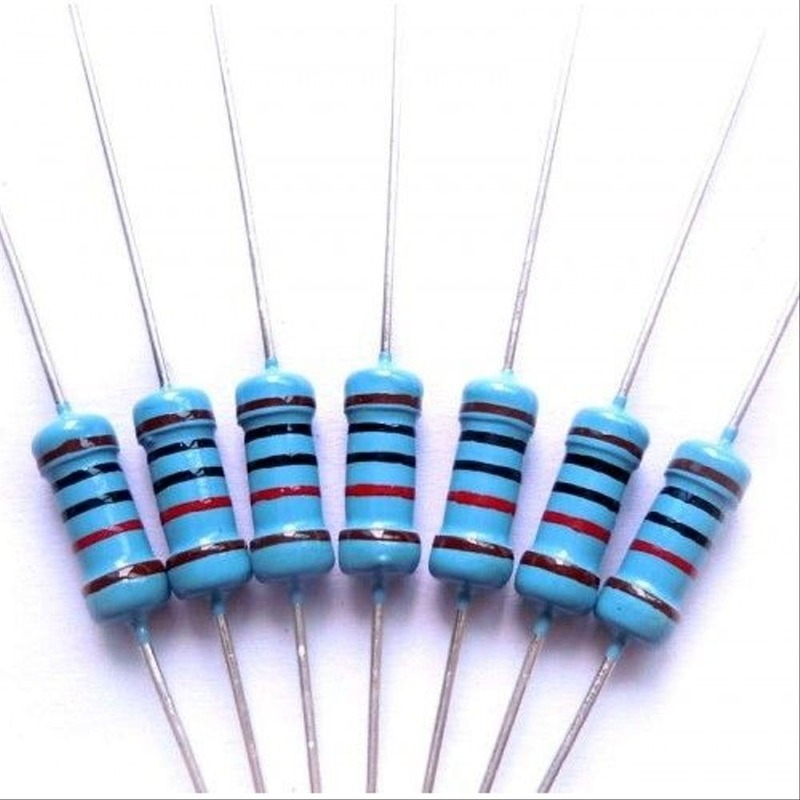
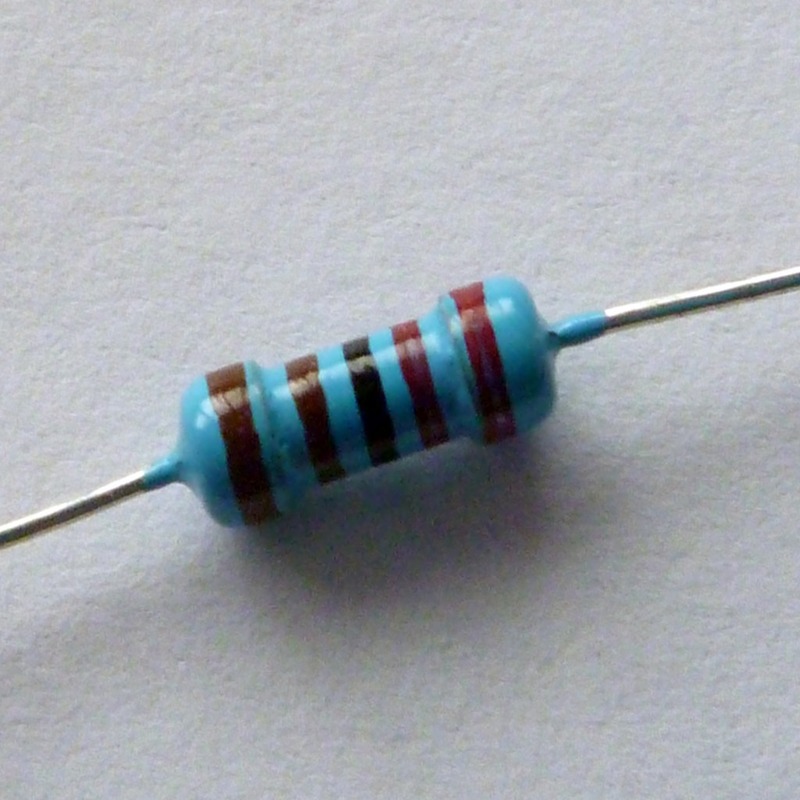
Resistor color codes help identify the resistance value of resistors, including the 2200 ohm variant. Understanding these codes is essential for anyone working with resistors in electronics. The color code system uses colored bands around the resistor body to indicate its resistance value, tolerance, and sometimes temperature coefficient.
Typically, a 2200 ohm resistor will have four or five colored bands. The first two or three bands represent significant figures, while the next band indicates the multiplier, and the last band provides the tolerance. For a 2200 ohm resistor, the color bands would typically look like this: Red (2), Red (2), Brown (multiplier of 10), and Gold (tolerance of ±5%).
To read these color codes correctly, use a color code chart or guide. Familiarizing yourself with the colors and their corresponding values will make identifying resistor values straightforward and efficient. This knowledge is particularly important when replacing resistors in electronic circuits where specifications matter.

Applications of 2200 Ohm Resistors
The 2200 ohm resistor is utilized in a multitude of applications across the electronics landscape. Understanding these applications helps technicians and engineers choose the right component for their specific needs. One significant use of this resistor is in the creation of voltage dividers. Voltage dividers utilize resistors to reduce voltage levels to safe limits necessary for different components. For instance, in interfaces connecting microcontrollers with sensors, a 2200 ohm resistor ensures that the voltage levels align with the microcontroller’s input requirements.
Another critical application involves current limiting in LED circuits. LEDs commonly require current limiting to prevent excessive current that could potentially damage the diode. In many instances, a 2200 ohm resistor is employed in these applications, ensuring the LED receives just the right amount of current for optimal brightness without burning out.
Signal conditioning is another area where the 2200 ohm resistor excels. In analog circuits, these resistors work in conjunction with capacitors to create filters that shape and manipulate signals to achieve desired outputs. For instance, in audio applications, filters can help eliminate unwanted noise while enhancing sound quality. A 2200 ohm resistor can significantly influence the performance of analog circuits, particularly those that process audio signals.
Additionally, the use of a 2200 ohm resistor is common in adjustable circuits. When used in conjunction with potentiometers, this resistor can vary electrical resistance according to the positioning. This functionality allows users to tailor circuit performance based on specific needs. Resistors like the 2200 ohm variant offer a broad range of adaptability, with many applications requiring specific adjustments based on operational requirements.
Selecting the Right Resistor for Your Project
When working on electronics projects, selecting the correct resistor for your application is critical for achieving the intended outcomes. Start by assessing the circuit requirements. Each circuit has specific voltage and current requirements that necessitate an appropriate resistor. A 2200 ohm resistor is beneficial for certain applications, but ensure you match it with the project’s specifications accurately.
Next, you should carefully consider the power rating. Make sure the resistor can tolerate the power it will encounter. It is advisable to select a resistor with a higher power rating than calculated. This approach creates a safety buffer as it protects the resistor from overheating and ensures circuit reliability.
Additionally, consider the environment where the resistor will operate. Resistors in hot or humid conditions might need specifications that accommodate those environmental factors. Resistors designed for high temperatures or humidity can significantly enhance circuit longevity and performance.
Another fundamental aspect is the availability of the resistor types. The 2200 ohm resistor can be found as both surface-mount devices and through-hole types. Your project’s PCB layout and design impacts which form factor will work best. Therefore, assessing physical dimensions and compatibility with existing components is crucial.

Practical Tips for Using Resistors Effectively
In addition to selecting the right resistor, knowing how to use them effectively is critical for circuit performance. When you solder resistors onto a PCB, ensure that you maintain proper orientation and placement to avoid incorrect connections. Often, resistors come with specific designations that should be adhered to. Always use appropriate soldering techniques to avoid overcooking the resistor, as excessive heat can damage its characteristics.
When building circuits with 2200 ohm resistors, always consider their interaction with other components. A good practice is to test circuits on a breadboard before finalizing design choices on a PCB. This allows you to verify that the resistor values meet the needs of the entire circuit under different input conditions. It also enables you to experiment with different resistor values to find the optimal setup, contributing to design efficiency.
Regularly verify the condition of your resistors in projects, especially in high-powered or critical circuits. If resistors have become damaged or overheated, they may change resistance values or fail completely. Employ a multimeter to check the resistance of 2200 ohm resistors periodically to ensure their functionality and reliability.
Conclusion: The Importance of the 2200 Ohm Resistor
In conclusion, the 2200 ohm resistor is essential in various electronic applications. Understanding its specifications and functions can help in successful circuit design. Whether utilized for voltage dividers, current limiting in LED circuits, or signal conditioning, the 2200 ohm resistor offers reliability and performance.
Selecting the right resistor allows you to achieve optimal performance and reliability. Tolerance, power rating, temperature coefficient, and other specifications impact how well the resistor will function in specific applications. Knowledge of resistor color codes ensures smooth identification, leading to fewer errors in component selection.
Moreover, the versatility of the 2200 ohm resistor opens up opportunities in circuit design. Take the time to experiment with different configurations and applications. The insights gained will significantly improve your understanding of electronics. Embrace the knowledge shared in this article and implement these concepts as you further explore the fascinating field of electronics. The 2200 ohm resistor is just the beginning, opening doors to countless possibilities in your projects ahead.
Investing time in learning about resistors will ultimately lead to greater success in your electronics endeavors. Embrace the opportunities that come with using this valuable component, and enhance your understanding of electronics. As you do, you will discover the immense value it contributes to both simple and complex electronic implementations.