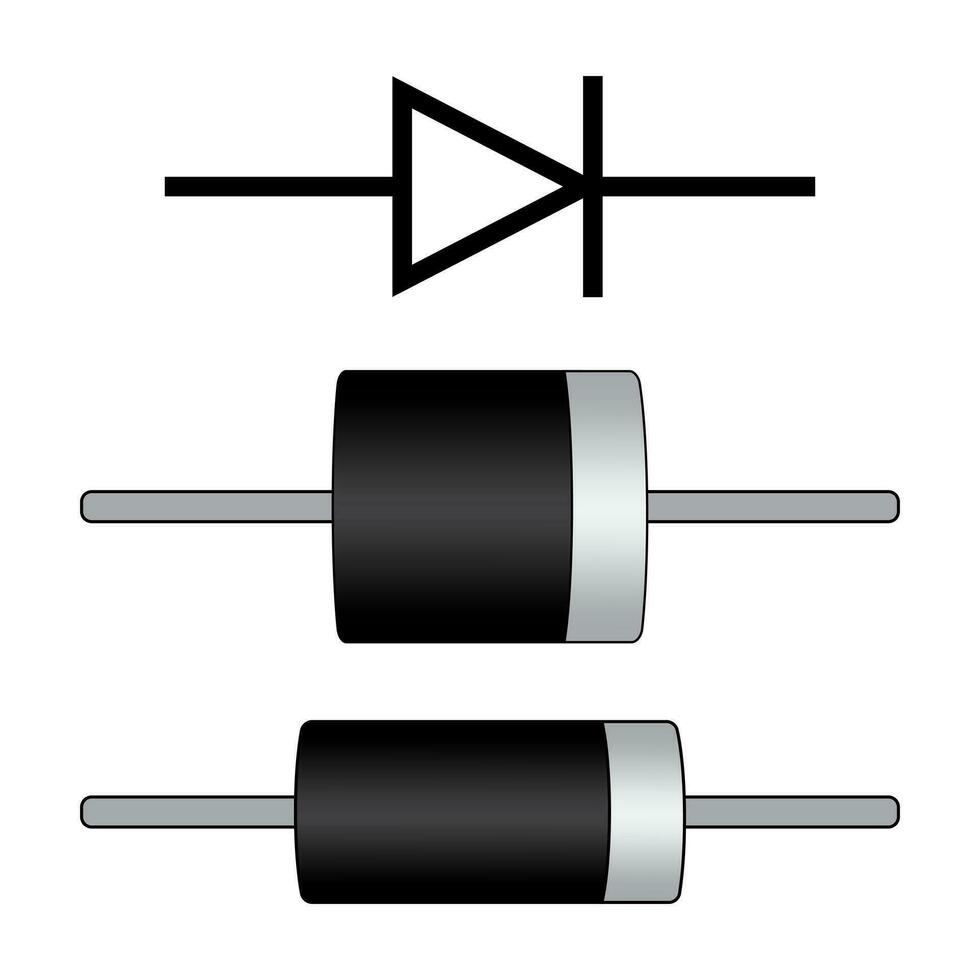
what is the purpose of a diode
Diodes are crucial components in the world of electronics. They are fundamental devices that play many roles in circuits. This article will explore their purpose, types, and applications. We will break down complex topics into simple segments. This way, all readers can easily understand the significance of diodes.What is a Diode?
 What is a Diode?
What is a Diode?
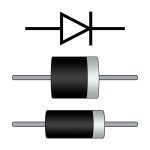
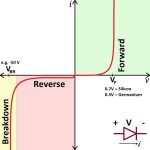
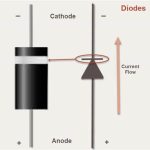
A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only. This unidirectional behavior makes it an essential component in various electronic applications. Diodes are usually made of silicon, but they can also be made from other materials, such as germanium.
Basic Structure of a Diode
A diode consists of two layers of semiconductor material. TThe p-type material has an abundance of holes (positive charge carriers), while the n-type material has an abundance of electrons (negative charge carriers). When these two materials join, they create a p-n junction.
How Diodes Work
This unique property is what makes diodes very important.
 Types of Diodes
Types of Diodes
what is the purpose of a diode
There are several types of diodes, each designed for specific functions. Understanding these types can help you understand their purposes better.
1. Standard Diodes
Standard diodes are used in most electronic circuits. They are primarily used for rectification, which converts alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC).
Purpose in Rectification
When AC voltage is applied to a standard diode, it only allows the positive half of the AC signal to pass through. This action prevents the negative half from passing, thereby converting AC to DC.
2. Zener Diodes
Zener diodes are designed to operate in reverse bias mode. They allow current to flow in the reverse direction when a specific voltage is reached, known as the Zener voltage.
Voltage Regulation
Zener diodes are primarily used for voltage regulation. By maintaining a constant voltage, they protect circuits from voltage spikes. This function is especially important in power supply circuits.
3. Schottky Diodes
Schottky diodes have a faster switching speed compared to standard diodes. They have low forward voltage drop, making them efficient in high-frequency applications.
Application in High-Speed Circuits
These diodes are commonly used in high-speed switching and RF applications. Their fast response time allows them to handle rapid changes in current effectively.
 4. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
4. Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs)
LEDs are a special type of diode that emit light when current flows through them. They are widely used in display technology and lighting solutions.
Purpose in Lighting and Displays
LEDs are energy-efficient and have a long lifespan. They are utilized in indicators, screens, and general lighting applications. Their ability to produce light makes them unique among other diodes.
Types of diodes:
Diodes come in various types, each with specific characteristics and applications. Here are some common types of diodes:
Standard Diode:
Used for rectification and general purposes. Commonly known as silicon diodes.
Zener Diode:
Designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when a specified voltage (Zener voltage) is reached. Used for voltage regulation.
Schottky Diode:
Known for its low forward voltage drop and fast switching speed. Commonly used in high-frequency applications and power rectification.
 Light Emitting Diode (LED):
Light Emitting Diode (LED):
Emits light when current flows through it. Widely used for display and lighting applications.
Photodiode:
Converts light into electrical current. Used in light detection and optical communication.
Varactor Diode (or Varicap):
Acts as a variable capacitor when reverse-biased. Used in tuning circuits.
Tunnel Diode:
Can operate at very high speeds due to quantum tunneling. Used in high-frequency applications.
Laser Diode:
Emits coherent light when current passes through it. Used in laser applications, such as in optical communications.
Avalanche Diode:
Designed to operate in reverse breakdown, offering high voltage and current protection. Used in surge protection.
PIN Diode: Used in radio frequency (RF) applications, it has a wide intrinsic layer that allows for variable impedance.
Each type of diode serves distinct functions in electronic circuits and systems.
 Applications of Diodes
Applications of Diodes
Diodes find application in various domains. Understanding these applications can clarify their importance in electronics.
1. Power Supply Circuits
Diodes are widely used in power supply circuits. They convert AC to DC, making them essential for battery chargers, power adapters, and electronic devices.
Role in Converting AC to DC
In power supplies, diodes rectify the input AC voltage to provide a stable DC output. This conversion ensures that electronic devices receive the correct voltage level for operation.
2. Signal Demodulation
Diodes are used in radio frequency applications for signal demodulation. They help recover audio signals from modulated radio waves.
Importance in Communication Systems
In communication systems, diodes play a crucial role in extracting information from carriers. This function is vital for radios and televisions.
3. Clamping and Clipping Circuits
what is the purpose of a diode
Diodes serve in clamping and clipping circuits to protect sensitive components from voltage spikes.
Protection Against Voltage Spikes
By restricting the voltage to a certain level, diodes prevent damage to circuits. This protection is essential in devices like computers and smartphones.
4. Surge Protection
Diodes are used as surge protectors in various devices. They help divert excess voltage away from sensitive electronics.
Keeping Devices Safe
When a surge occurs, diodes absorb the extra voltage, preventing damage to the device. This mechanism is commonly found in home electronics and industrial equipment.
Advantages of Diodes
Understanding the advantages of diodes helps appreciate their role in electronics. They offer many benefits, making them indispensable.
1. Unidirectional Current Flow
Diodes allow current to flow in one direction only. This property is crucial for many applications, ensuring circuits function correctly.
2. Voltage Regulation
Certain types of diodes, like Zener diodes, provide voltage regulation. They stabilize voltage levels, protecting circuits from fluctuations.
3. Compact Size
Diodes are small devices, which allows for the creation of compact electronic circuits. Their size makes them easy to integrate into various products.
4. Low Cost
Diodes are inexpensive components. Their affordability makes them accessible for different applications in consumer electronics and industrial systems.
5. Long Longevity
Diodes have a long operational lifespan. Their durability contributes to the reliability of electronic devices.
Challenges of Using Diodes
what is the purpose of a diode
While diodes have many advantages, they do present challenges. Recognizing these challenges is essential for effective use.
1. Limited Current Ratings
Each diode has a maximum current rating. Exceeding this limit can damage the diode, leading to circuit failure.
2. Voltage Drop
Diodes introduce a voltage drop during operation. This drop can affect the efficiency of circuits, especially in low-voltage applications.
3. Temperature Sensitivity
Diodes can be sensitive to temperature changes. High temperatures can affect their performance and reliability.
Future of Diodes
The future of diodes is promising.
1. Advancements in Materials
New materials, like gallium nitride (GaN), are being researched. These materials can provide higher efficiency and better performance compared to traditional silicon diodes.
2. Increased Applications in Emerging Technologies
As technology evolves, the application of diodes is expanding. Used in electric cars, renewable energy systems, and advanced communication technologies.
3. Smart Diodes
They can optimize performance in real-time, making them a topic of interest for researchers.
Conclusion
In summary, diodes are fundamental components in electronic circuits. They serve vital purposes, from rectification and voltage regulation to protection against voltage spikes. The various types of diodes offer unique functionalities that make them applicable across multiple domains.
Understanding diodes allows us to appreciate their role in modern technology. As advancements continue, we can expect diodes to become even more efficient and versatile.