What is a Resistor? Understanding its Importance in Electronics
When delving into electronics, one cannot overlook the vital role of resistors. But what is a resistor? Simply put, resistors are passive electrical components that limit the flow of electric current in a circuit. They are essential for controlling voltage and current levels, ensuring circuits operate effectively and safely. This comprehensive guide will examine resistors, their types, functions, applications, and how they fit into the broader realm of electronic components.Learn its types, functions, and importance in electronic circuits. Understand the resistor color code and how to use resistors.
Understanding Resistors
In an electronic circuit, resistors play a key role. As a passive component, a resistor does not produce energy; rather, it dissipates energy as heat. This fundamental property allows resistors to control the flow of electric current. The unit of measurement for resistance is the ohm (Ω), named after German physicist Georg Simon Ohm. The higher the resistance value, the less current will flow for a given voltage.
Resistors maintain the stability of electronic circuits. Without them, devices could malfunction due to excessive current. This management of electrical flow is critical not only in everyday electronics but also in complex systems such as computers and telecommunications.

Types of Resistors
There are several types of resistors, each serving different applications and functions. Understanding these types helps users select the right resistor for their projects.
Fixed Resistors
Fixed resistors have a defined resistance value that does not change. They are the most common type of resistors found in circuits. Their simplicity makes them suitable for various applications, particularly in voltage division and current limiting. For example, a 1kΩ fixed resistor can drop the voltage in a circuit to protect sensitive components.
Variable Resistors
Variable resistors, such as potentiometers, allow users to adjust their resistance. This adjustability can enhance functionality in applications like audio equipment, where users can change volume levels. There are two primary types of variable resistors:
-
Potentiometers: These have three terminals and enable continuous voltage adjustment.
-
Rheostats: These are used for high currents and only have two terminals.
Both types of variable resistors offer flexibility in electronic design, making them popular in various products.
Special Resistors
Special resistors include components such as thermistors and photoresistors, which have unique operational characteristics:
-
Thermistors: These resistors change resistance with temperature variations. Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) thermistors decrease resistance as the temperature rises, while Positive Temperature Coefficient (PTC) thermistors increase resistance with temperature.
-
Photoresistors (LDR): Light-dependent resistors change resistance based on light exposure. As light intensity increases, their resistance decreases, making them ideal for light-sensing applications, such as automatic street lights.
Wirewound Resistors
Wirewound resistors consist of a wire coil wrapped around a ceramic core. They excel in high-power applications due to their ability to dissipate heat effectively. These resistors typically offer high accuracy and stability, making them valuable in industrial settings.
Resistor Functions: Why They Matter
Resistors fulfill several critical functions in electronic circuits. Recognizing these roles helps clarify their significance in design and functionality.
Current Limitation
One of the principal functions of resistors is to limit current. This is crucial in protecting sensitive components. For example, a resistor can prevent excess current from flowing into an LED, ensuring its longevity. By using Ohm’s law, which states that \( V = I \times R \) (voltage = current x resistance), circuit designers can calculate the appropriate resistance needed to limit current effectively.
Voltage Division
Resistors can create voltage dividers, allowing parts of a circuit to function at different voltage levels. This process is fundamental in various applications, especially in analog signal processing. By carefully placing resistors in series, specific voltage levels can be delivered to particular components.
Signal Conditioning
Resistors can improve signal quality in circuits. They can filter unwanted frequencies, shaping signals to suit specific requirements. This signal conditioning is vital in communication systems, audio equipment, and sensor interfaces, ensuring that signals are clean and usable.
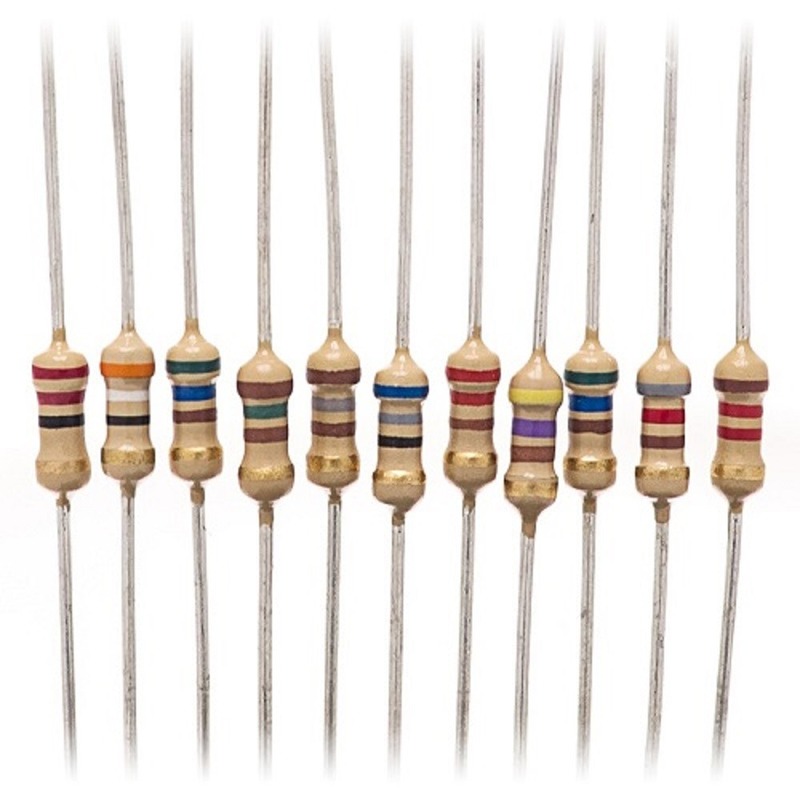

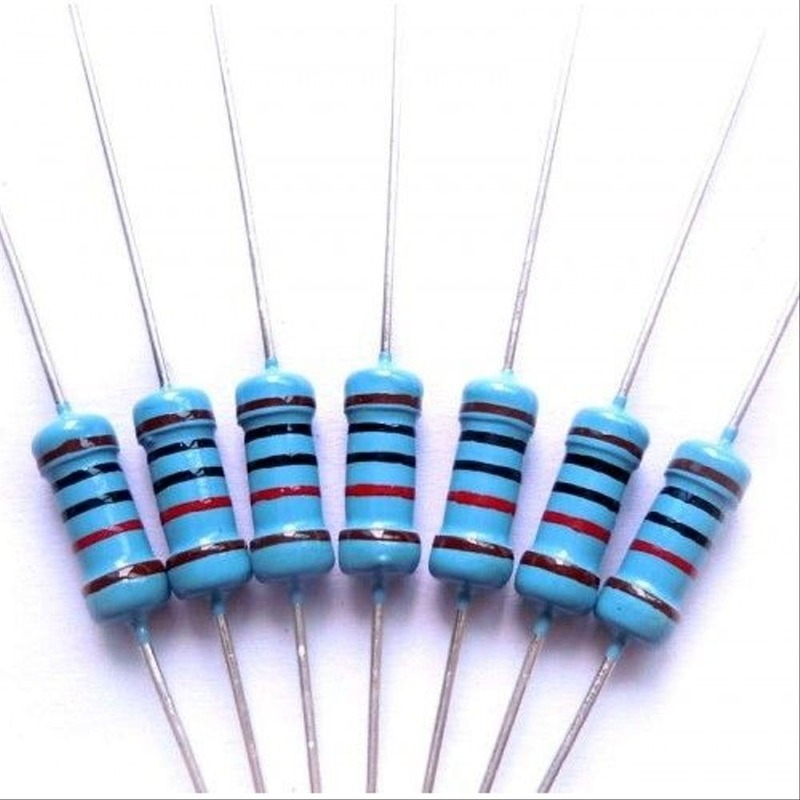
Understanding Resistor Values: The Color Code System
Reading resistor values accurately is essential for anyone working with electronic circuits. The color code system is a widely used method for representing resistance values.Learn its types, functions, and importance in electronic circuits. Understand the resistor color code and how to use resistors.
Reading the Color Code
Each resistor has colored bands that denote its resistance value. Typically, a standard resistor will have four color bands. Here’s a breakdown of what each color represents:
-
First Band: Represents the first digit of the resistance value.
-
Second Band: Represents the second digit.
-
Third Band: Represents the multiplier (number of zeros to add).
-
Fourth Band: Indicates tolerance (how much the actual resistance can vary from the stated value).
Example
For example, a resistor with bands of red, red, brown, and gold would be read as follows:
-
Red (2)
-
Red (2)
-
Brown (x10^1)
-
Gold (±5% tolerance)
This resistor would have a value of 220 ohms with a tolerance of ±5%.
Visual Reference
Including a visual chart of the resistor color code can significantly enhance understanding. This chart serves as a quick reference, making it easier for users to decode resistor values accurately.
Resistor Applications in Electronics
Resistors are ubiquitous in electronic circuits, serving multiple purposes across various applications. Let’s highlight some common uses:
Power Supplies
In power supply circuits, resistors ensure that the voltage levels meet specifications, preventing damage to components. By controlling the current flowing into delicate components, they safeguard the entire circuit.
Amplifiers
In audio amplifiers, resistors help manage gain levels. By creating voltage dividers, they allow designers to set amplification factors, thus influencing audio output.
Signal Conditioning Circuits
Resistors play a prominent role in signal conditioning. They allow designers to filter and clean signals, ensuring that interference is minimized. This application is crucial in environments where clear signals are paramount.

Differences Between Resistors and Other Components
To appreciate resistors fully, it’s essential to understand how they differ from other electronic components, particularly capacitors.
Comparing Resistors and Capacitors
Resistors and capacitors are both vital components in circuits, yet they have different functionalities. While resistors limit current, capacitors store and release energy. This fundamental difference can be illustrated through their respective uses in circuits:
-
Resistors: Primarily control current and voltage levels.
-
Capacitors: Store energy to release it when required. They can smooth out fluctuations in power supply, serving different roles compared to resistors.
Complementary Roles in Circuits
While resistors and capacitors serve distinct functions, they complement each other in many circuits. For example, in timing circuits, capacitors and resistors often work together to produce time delays, allowing engineers to design effective timing solutions.
Conclusion: The Role of Resistors in Technology
In summary, resistors are fundamental components in electronics, helping manage current flow, voltage levels, and signal integrity. Their ability to limit current, facilitate voltage division, and enhance signal quality makes them indispensable in various applications. Understanding what a resistor is and how it functions is crucial for students, hobbyists, and professionals alike.What is a resistor, Learn its types, functions, and importance in electronic circuits. Understand the resistor color code and how to use resistors.
By familiarizing yourself with resistor types, functions, and applications, you can significantly expand your knowledge of electronics. As you explore circuits further, remember the pivotal role resistors play in technological advancements. If you have any questions or insights regarding resistors and their usage, feel free to share them in the comments below!