Introduction
Introduction
who invented the light emitting diode
The light-emitting diode, commonly known as LED, has revolutionized the world of lighting with its energy-efficient and durable characteristics. But have you ever wondered who the brilliant mind behind this innovative technology is? In this comprehensive exploration, we will delve into the story behind the invention of the light-emitting diode, shedding light on the remarkable discovery that has transformed the way we illuminate our world.
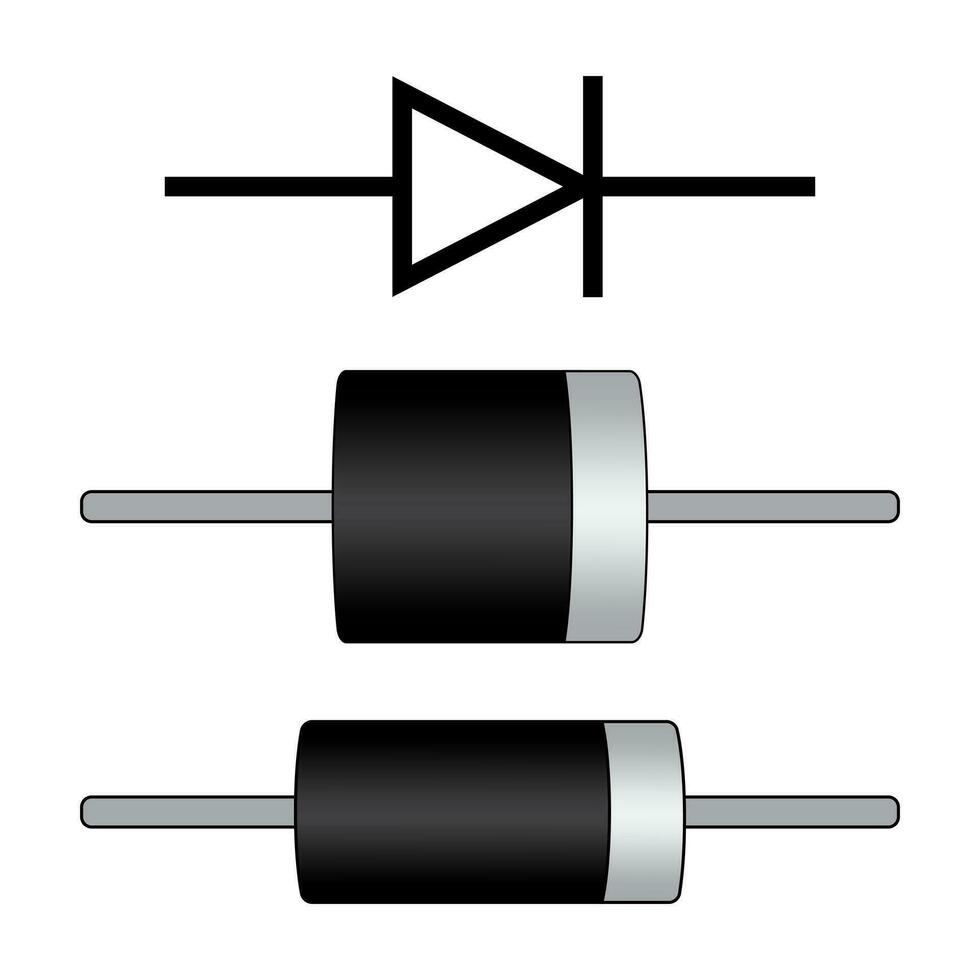
 The primary function of a diode can be summarized as follows:
The primary function of a diode can be summarized as follows:
Current direction control:
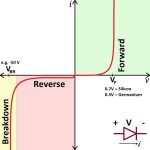
A diode allows the current to flow in only one direction (forward bias) while blocking it in the opposite direction (reverse bias). This property is fundamental for converting AC to DC and for preventing the reverse flow of current in electronic circuits.
Rectification:
Diodes are crucial components in rectifier circuits, where they convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction.
Voltage regulation:
Diodes are used in voltage regulators to stabilize and regulate the voltage levels in electronic circuits.
Signal demodulation:
In communication systems, diodes are utilized for signal demodulation, extracting the original modulated signal from the carrier wave.
Overvoltage protection:
Diodes are employed in circuits to protect electronic components from damage due to reverse voltage or voltage spikes.
Early Innovations in Electroluminescence
To understand the invention of the light-emitting diode, we need to look back at the early innovations in electroluminescence. The phenomenon of electroluminescence, where a material emits light in response to an electric current, laid the groundwork for the development of the light-emitting diode. Early experiments in this area set the stage for the groundbreaking discovery that would eventually lead to the creation of the LED.
 The Contribution of Oleg Losev
The Contribution of Oleg Losev
One of the pioneering figures in the development of the light-emitting diode was the Russian scientist Oleg Vladimirovich Losev. In the 1920s, Losev conducted extensive research on semiconductor materials and their electroluminescent properties. His work led to the invention of the first LED-like device, although it was not initially recognized as such. Losev’s contributions to the understanding of semiconductors and electroluminescence laid the foundation for future advancements in LED technology.
Creation of the First Visible-spectrum LED
In 1962, Holonyak, working at General Electric, successfully created the first practical LED that emitted visible red light. This pivotal moment marked a major advancement in the evolution of LED technology.
 Advancements in LED Technology
Advancements in LED Technology
Following the creation of the first visible-spectrum LED, further advancements in LED technology rapidly ensued. Scientists and engineers around the world continued to refine and expand the capabilities of light-emitting diodes, leading to the development of LEDs capable of emitting light across the entire visible spectrum. These advancements propelled the widespread adoption of LEDs in various applications, including lighting, displays, and technology.
Impact and Applications of LEDs
The impact of the invention of the light-emitting diode cannot be overstated. LEDs have revolutionized the lighting industry, offering superior energy efficiency, longevity, and versatility compared to traditional lighting technologies. Additionally, LEDs have found wide-ranging applications in electronics, signage, displays, and countless other fields, contributing to significant advancements in technology and energy conservation.
Future Innovations and Discoveries
As the technology behind light-emitting diodes continues to advance, ongoing research and innovation promise even greater breakthroughs in the field of LED technology. Scientists and engineers are exploring new materials, designs, and applications for LEDs, paving the way for future discoveries that will further enhance the capabilities and potential of this groundbreaking lighting technology.
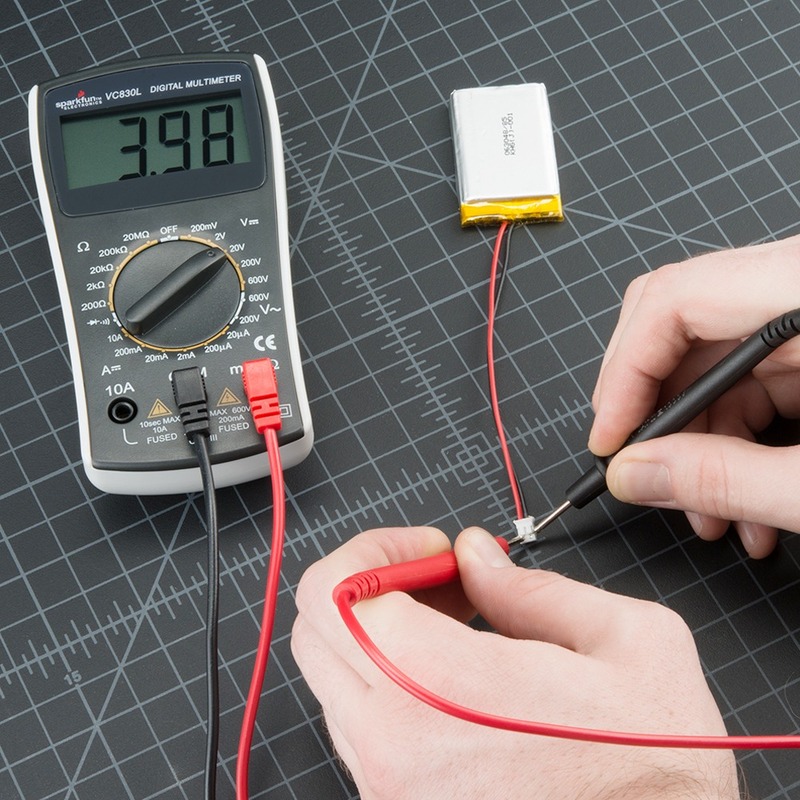
To test a diode, you can follow these steps:
Set your multimeter to the diode test mode (usually denoted by a diode symbol).
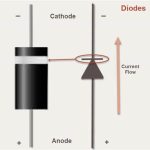
Place the positive (red) probe on the anode of the diode and the negative (black) probe on the cathode.
The multimeter will forward bias the diode and display a voltage drop if it’s functioning properly. A typical silicon diode will show a voltage drop of around 0.6 to 0.7 volts.
Reverse the probes, placing the positive probe on the cathode and the negative probe on the anode. The multimeter should indicate an open circuit or a very high resistance, showing that the diode is not conducting in reverse bias.
If the diode passes these tests, it should be functioning correctly. Measure a diode using a multimeter
To measure a diode using a multimeter, follow these steps:
Identify the anode and cathode of the diode.
Connect the positive (red) probe of the multimeter to the anode of the diode and the negative (black) probe to the cathode.
In forward bias, a working diode should display a voltage drop, typically around 0.6 to 0.7 volts, on the multimeter.
Reverse the probes, placing the positive probe on the cathode and the negative probe on the anode. A functioning diode should show an open circuit or a very high resistance, indicating it is not conducting in reverse bias.
By following these steps, you can test a diode to determine if it is functioning properly.
 The popular trends in Emitting Diodes (LEDs) include:
The popular trends in Emitting Diodes (LEDs) include:
who invented the light emitting diode
Energy efficiency:
There is a growing emphasis on the development of more energy-efficient LEDs, leading to reduced power consumption and lower environmental impact.
Smart lighting:
The integration of LEDs with smart technology, such as wireless connectivity and advanced control systems, is a popular trend, enabling customizable and energy-efficient lighting solutions.
Human-centric lighting:
There is increased focus on developing LED lighting solutions that mimic the natural light spectrum to provide better lighting quality and support human well-being and productivity.
Increased lifespan:
Ongoing research and development aim to further improve the lifespan of LEDs, contributing to their long-term sustainability and reduced maintenance requirements.
Some considerations for Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) include:
Correct handling: LEDs are sensitive to static electricity, so it’s essential to handle them with care and use proper grounding techniques to avoid damaging the components.
Voltage and current requirements: LEDs require specific voltage and current levels for optimal operation, so it’s crucial to adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications and use appropriate driver circuits and power supplies.
ESD protection: Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage LEDs, so it’s important to implement ESD protection measures during handling and installation.
Environmental factors: LEDs can be sensitive to moisture and extreme temperatures, so it’s important to consider environmental conditions when designing and installing LED lighting systems.
Compatibility with dimming controls: When using dimmable LED products, ensure compatibility with the chosen dimming control system to avoid potential flickering or compatibility issues.
Quality assurance: Selecting high-quality LEDs from reputable manufacturers can ensure reliability, consistency, and performance.
By considering these factors, users can optimize the performance, longevity, and safety of Light Emitting Diodes in various applications.
Conclusion
who invented the light emitting diode
The invention of the light-emitting diode represents a pivotal moment in the history of technology and lighting. From the early experiments in electroluminescence to the pioneering work of Oleg Losev and Nick Holonyak Jr., the evolution of LEDs has revolutionized the way we illuminate our world. As we look to the future, the ongoing advancements and discoveries in LED technology continue to enhance its capabilities, paving the way for a brighter, more energy-efficient, and sustainable future.