 Introduction:
Introduction:
The blower motor resistor plays a crucial role in the functionality of a vehicle’s heating and air conditioning system. When this component malfunctions, it can lead to a variety of issues that affect the operation of the blower motor. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the common symptoms of a faulty blower motor resistor. By recognizing these signs, vehicle owners can quickly identify and address any issues, ensuring the comfort and functionality of their heating and air conditioning system.
There are primarily two types of blower motor resistors commonly used in automotive HVAC systems:
Thermal Blower Motor Resistor:
Also known as a thermal limit switch or thermal fuse, this type of blower motor resistor works by using a bimetallic strip or a temperature-sensitive component to control the current flow. When the blower motor operates at a high speed, it generates heat. The thermal blower motor resistor senses this heat and uses the bimetallic strip or temperature-sensitive component to interrupt the electrical current and protect the blower motor from overheating. Once the temperature decreases, the circuit reconnects, allowing the blower motor to resume operation.
Electronic Blower Motor Resistor:
This type of blower motor resistor utilizes solid-state components, specifically transistors or power modules, to control the current flow to the blower motor. The electronic blower motor resistor provides precise control over the fan speed by adjusting the amount of current passing through the blower motor. It achieves this by changing the resistance value electronically based on signals received from the HVAC control unit. The electronic blower motor resistor offers smoother and more consistent fan speed control compared to the thermal resistor.
The choice of blower motor resistor type depends on the specific vehicle application and the desired functionality of the HVAC system. Thermal resistors are commonly used in older vehicles, while electronic resistors are prevalent in modern vehicle models.
Understanding the Blower Motor Resistor
Function of the Blower Motor Resistor:
The blower motor resistor regulates the speed at which the blower motor operates.
It controls the flow of electrical current to the blower motor, allowing for different fan speeds.
Location of the Blower Motor Resistor:
The blower motor resistor is typically located near the blower motor itself or in the HVAC system’s ductwork.
It may be accessible from under the dashboard or behind the glove compartment.
 Common Symptoms of a Faulty Blower Motor Resistor
Common Symptoms of a Faulty Blower Motor Resistor
Inoperative Blower Motor:
If the blower motor fails to turn on or runs intermittently, it may indicate a problem with the blower motor resistor.
The motor may only work on the highest fan speed setting or not work at all.
Inconsistent or Erratic Fan Speeds:
A faulty blower motor resistor can cause inconsistent airflow from the vents.
The fan speed may fluctuate or change unexpectedly, even when the controls are set to a specific level.
Limited or No Blower Motor Settings:
When the blower motor resistor fails, some or all of the fan speed settings may become unavailable.
Drivers may only have access to the highest setting or, in some cases, no fan speed options at all.
Other Indicators of a Faulty Blower Motor Resistor
Overheating Resistors:
A faulty blower motor resistor can overheat, leading to a burning smell coming from the vents or within the vehicle cabin.
This overheating can result in a potential fire hazard and should be addressed immediately.
Melted or Damaged Wiring:
In severe cases, a malfunctioning blower motor resistor may cause damage to the associated wiring.
Signs of melted or damaged wiring may be visible near the resistor or in the HVAC system’s control panel.
 Causes of Blower Motor Resistor Failure
Causes of Blower Motor Resistor Failure
Excessive Heat:
The blower motor resistor is exposed to heat generated by the blower motor during operation.
Over time, this constant exposure to heat can cause the resistor to degrade and eventually fail.
Electrical Overload:
An electrical overload, often caused by a faulty blower motor or related system components, can damage the blower motor resistor.
Excess current flowing through the resistor can cause it to burn out or fail prematurely.
Fixing a Faulty Blower Motor Resistor
Replacement of the Resistor:
When a blower motor resistor fails, it is generally recommended to replace the component.
Refer to the vehicle’s service manual or consult a qualified technician for guidance on locating and replacing the resistor.
Inspection and Repair of Related Components:
In addition to replacing the blower motor resistor, it is essential to inspect the blower motor and associated wiring for any signs of damage.
Addressing any underlying issues can prevent further failures and ensure optimal performance.
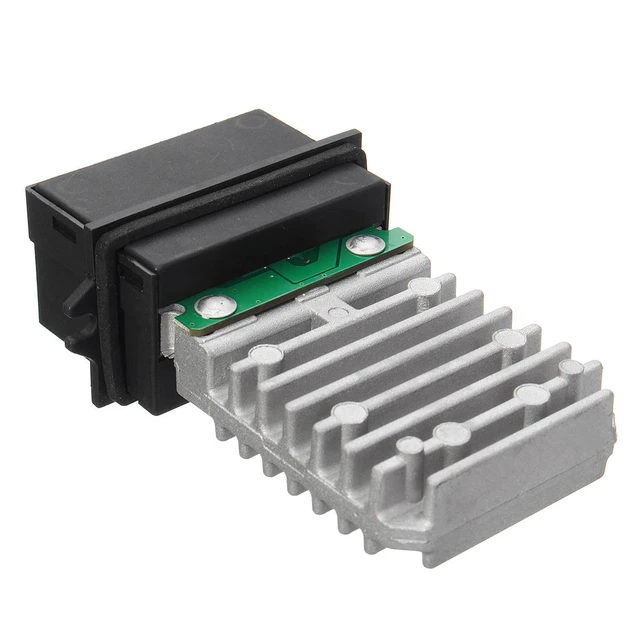 Working principle of blower motor resistor
Working principle of blower motor resistor
How does the blower motor resistor work? The blower motor resistor is a component found in HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems in vehicles. Its main function is to control the speed of the blower motor, which regulates the airflow inside the vehicle’s cabin. The blower motor resistor operates based on the principle of electrical resistance.
The blower motor resistor is typically made up of multiple resistors and a control module. These resistors are responsible for creating different levels of electrical resistance. The control module, often located near the blower motor, receives signals from the HVAC control unit and adjusts the blower motor speed accordingly.
When the HVAC control unit is set to a particular fan speed, it sends an electrical signal to the blower motor resistor. This signal is interpreted by the control module, which determines the appropriate amount of resistance needed to achieve the desired speed. The control module then adjusts the current flowing to the blower motor by selectively activating or deactivating the resistors.
By changing the resistance, the blower motor resistor effectively controls the voltage supplied to the blower motor. As a result, the blower motor spins at different speeds, allowing for varied airflow inside the cabin. The higher the resistance, the slower the blower motor rotates, and the lower the airflow. Conversely, lower resistance leads to higher fan speeds and increased airflow.
In summary, the blower motor resistor operates by regulating the electrical resistance within the circuit, which, in turn, controls the speed of the blower motor. This enables the HVAC system to provide the desired airflow for heating, cooling, and ventilation purposes inside the vehicle’s cabin.
 Conclusion:
Conclusion:
The blower motor resistor is a vital component of a vehicle’s heating and air conditioning system. By recognizing the common symptoms of a faulty blower motor resistor, vehicle owners can take necessary steps to address any issues promptly. Whether it’s an inoperative blower motor, inconsistent fan speeds, or limited fan settings, identifying these signs allows for timely repairs or replacements. Consultation with a qualified technician is advised for proper diagnosis and repair. By maintaining a properly functioning blower motor resistor, users can ensure optimal comfort and functionality within their vehicles’ climate control systems.










